

1. วัตถุประสงค์#
บทความนี้จะแนะนำขั้นตอนการออกแบบและพัฒนา RESTful API สำหรับจัดการทรัพยากร ผู้ใช้งาน (Users), สินค้า (Products), คำสั่งซื้อ (Orders) และทรัพยากรแบบซ้อน (Nested Resources) เพื่อแสดงข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมดของผู้ใช้งาน และสินค้าทั้งหมดที่อยู่ในคำสั่งซื้อ โดยใช้ Node.js และ Express ร่วมกับ Prisma ซึ่งเป็น ORM (Object Relational Mapper) ที่จะช่วยให้เราทำงานกับฐานข้อมูล MySQL พร้อมทดสอบด้วย Postman
2. ติดตั้งโปรแกรมและตั้งค่าฐานข้อมูล#
-
ติดตั้ง Node.js version LTS ดาวน์โหลด Node.js เวอร์ชัน LTS (Long Term Support) จาก https://nodejs.org ↗ เลือกเวอร์ชัน LTS ที่แนะนำสำหรับการใช้งานในการพัฒนา
การตั้งค่า:
- ดาวน์โหลดไฟล์ installer ที่เหมาะสมกับระบบปฏิบัติการ (Windows, macOS, หรือ Linux)
- ติดตั้งโดยการดับเบิลคลิกไฟล์ installer และปฏิบัติตามขั้นตอนการติดตั้ง
- หลังจากติดตั้งเสร็จสิ้น ให้เปิด Command Prompt หรือ Terminal และตรวจสอบการติดตั้งด้วยคำสั่ง:
bashnode --version npm --version - ถ้าติดตั้งสำเร็จ จะแสดงเวอร์ชันของ Node.js และ npm
-
ติดตั้ง XAMPP (MySQL + phpMyAdmin) ดาวน์โหลดและติดตั้ง XAMPP จาก https://www.apachefriends.org ↗ เลือกเวอร์ชันที่เหมาะสมกับระบบปฏิบัติการ
การตั้งค่า:
- เมื่อติดตั้งเสร็จสิ้น ให้เปิด XAMPP Control Panel และตั้งค่า Apache และ MySQL ให้เป็น Service ดังภาพ
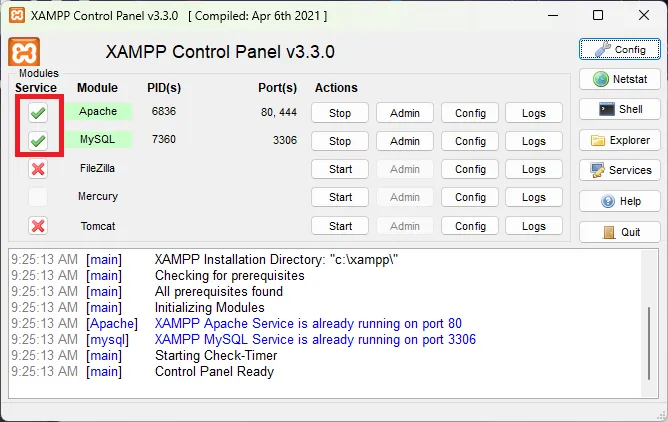
- Start บริการ Apache และ MySQL เพื่อให้สามารถใช้งานเว็บเซิร์ฟเวอร์และฐานข้อมูลได้
- เปิดเว็บเบราว์เซอร์ไปที่ http://localhost/phpmyadmin ↗
- คลิกที่แท็บ Databases
- ในส่วน Create database ให้ตั้งชื่อฐานข้อมูลว่า
express_prisma_dbแล้วคลิก Create
- เมื่อติดตั้งเสร็จสิ้น ให้เปิด XAMPP Control Panel และตั้งค่า Apache และ MySQL ให้เป็น Service ดังภาพ
-
ติดตั้ง Postman ดาวน์โหลด Postman ได้ที่ https://www.postman.com/downloads/ ↗ ติดตั้งและเปิดใช้งาน Postman จะใช้ Postman ในการทดสอบ API endpoints (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
การตั้งค่า:
- เปิด Postman และสร้าง Workspace ใหม่ เพื่อจัดเก็บ API endpoints
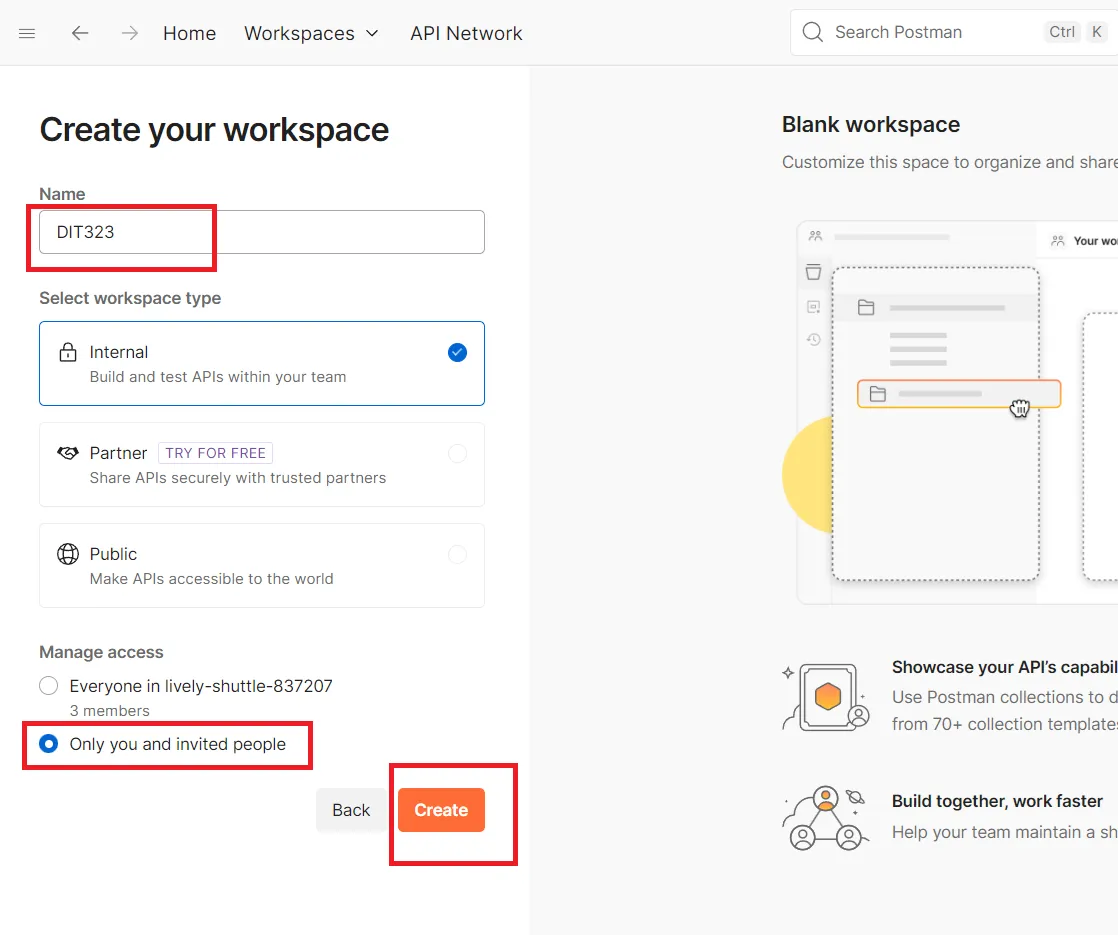
- เปิด Postman และสร้าง Workspace ใหม่ เพื่อจัดเก็บ API endpoints
3. ตั้งค่าโปรเจคและติดตั้ง Prisma#
-
สร้างโปรเจค Node.js เปิด Terminal หรือ Command Prompt แล้วรันคำสั่งเหล่านี้:
bashmkdir api-prisma cd api-prisma npm init -y npm install express cors body-parser code . # เปิด VS Code ในโฟลเดอร์โปรเจกต์ (ถ้าติดตั้ง) -
ติดตั้ง Prisma Prisma เป็น ORM ที่จะช่วยให้เราสามารถโต้ตอบกับฐานข้อมูลได้ง่ายขึ้นโดยไม่ต้องเขียน SQL โดยตรง
bashnpm install prisma --save-dev npx prisma init npm install @prisma/client -
ตั้งค่าไฟล์
.envหลังจากรันnpx prisma initจะมีไฟล์.envถูกสร้างขึ้นมาโดยอัตโนมัติ ให้แก้ไขDATABASE_URLในไฟล์.envให้ชี้ไปยังฐานข้อมูล MySQL ที่เราสร้างไว้:
plaintextDATABASE_URL="mysql://root:@localhost:3306/express_prisma_db"root: ชื่อผู้ใช้ฐานข้อมูล (ค่าเริ่มต้นของ XAMPP)@: รหัสผ่าน (เว้นว่างไว้สำหรับ XAMPP ถ้าไม่ได้ตั้งค่า)localhost:3306: Host และ Port ของ MySQLexpress_prisma_db: ชื่อฐานข้อมูลที่เราสร้างไว้
-
ติดตั้ง extension Prisma ใน VS Code เพื่อให้รองรับการเขียนไฟล์ .prisma
4. Prisma คืออะไร?#
Prisma คือ ORM (Object Relational Mapper) สำหรับ Node.js และ TypeScript ที่ช่วยให้สามารถทำงานกับฐานข้อมูลโดยใช้ JavaScript objects และ functions แทนการเขียน SQL raw queries โดยมีสมบัติหลักดังนี้:
- Generates types and client functions from your schema: สร้าง TypeScript types และ client functions โดยอัตโนมัติจาก Prisma schema ทำให้การเขียนโค้ดปลอดภัยและมี IntelliSense
- Supports migrations: จัดการการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้างฐานข้อมูลอย่างเป็นระบบ
- Supports relations between tables: จัดการความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างตารางต่างๆ ได้ง่ายขึ้น
5. กำหนด Models ใน prisma/schema.prisma#
ไฟล์ prisma/schema.prisma คือหัวใจสำคัญของ Prisma ที่ใช้ในการกำหนดโครงสร้างฐานข้อมูล (Database Schema) ของเรา
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
}
datasource db {
provider = "mysql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}5.1 User Model#
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
fname String
lname String
username String @unique // เพิ่ม @unique เพื่อให้ username ไม่ซ้ำกัน
email String @unique // เพิ่ม @unique เพื่อให้ email ไม่ซ้ำกัน
avatar String? // เพิ่ม ? เพื่อระบุว่า field นี้อาจเป็น null ได้
orders Order[]
}User: แทนข้อมูลผู้ใช้งาน (เช่น ลูกค้า)id: Primary Key และจะเพิ่มค่าอัตโนมัติfname,lname,username,email,avatar: ข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลของผู้ใช้งาน@unique: ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าusernameและemailไม่ซ้ำกันString?:avatarสามารถเป็นค่าว่าง (nullable) ได้
orders Order[]: ความสัมพันธ์แบบ One-to-Many หมายถึงผู้ใช้หนึ่งคนสามารถมีคำสั่งซื้อได้หลายรายการ นี่คือ Inverse Relation ของOrder.user
5.2 Product Model#
model Product {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
name String
price Int
orders OrderProduct[]
}Product: แทนข้อมูลสินค้าที่สามารถสั่งซื้อได้id: Primary Key และเพิ่มค่าอัตโนมัติname,price: รายละเอียดของสินค้าorders OrderProduct[]: ความสัมพันธ์แบบ Many-to-Many ผ่านตารางOrderProductหมายถึงสินค้าหนึ่งชิ้นสามารถอยู่ในหลายคำสั่งซื้อได้
5.3 Order Model#
model Order {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
userId Int
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
products OrderProduct[]
}Order: แทนข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อของลูกค้าid: Primary KeyuserId: Foreign Key ที่เชื่อมโยงกับUsermodeluser User @relation(...): ความสัมพันธ์แบบ Many-to-One หมายถึงแต่ละคำสั่งซื้อจะถูกสร้างโดยผู้ใช้เพียงคนเดียวproducts OrderProduct[]: ความสัมพันธ์แบบ Many-to-Many ผ่านตารางOrderProductหมายถึงคำสั่งซื้อหนึ่งรายการสามารถมีสินค้าได้หลายชิ้น
5.4. OrderProduct Model (Join Table)#
model OrderProduct {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
orderId Int
productId Int
order Order @relation(fields: [orderId], references: [id])
product Product @relation(fields: [productId], references: [id])
}OrderProduct: เป็นตารางเชื่อม (Join Table) สำหรับความสัมพันธ์ Many-to-Many ระหว่างOrderและProduct- แต่ละแถวในตารางนี้จะเชื่อมโยงหนึ่งคำสั่งซื้อเข้ากับหนึ่งสินค้า
order: เชื่อมโยงกับตารางOrderผ่านorderIdproduct: เชื่อมโยงกับตารางProductผ่านproductId
การตั้งค่านี้ช่วยให้:
- หนึ่งคำสั่งซื้อสามารถมีสินค้าได้หลายรายการ
- หนึ่งสินค้าสามารถเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของหลายคำสั่งซื้อได้
5.5 สรุปความสัมพันธ์ของ Models#
| Model | Relation Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| User | has many Orders | One-to-Many |
| Order | belongs to one User | Many-to-One |
| Order | has many Products via OrderProduct | Many-to-Many |
| Product | appears in many Orders via OrderProduct | Many-to-Many |
| OrderProduct | connects Order and Product | Join table |
6. สร้างและ Migrate ฐานข้อมูล#
หลังจากกำหนด schema.prisma แล้ว ให้รันคำสั่งนี้เพื่อสร้างตารางในฐานข้อมูล MySQL และสร้าง Prisma Client:
npx prisma migrate dev --name initคำสั่งนี้จะ:
- สร้างไฟล์ migration ในโฟลเดอร์
prisma/migrations - สร้างตารางตามที่กำหนดใน
schema.prismaในฐานข้อมูลexpress_prisma_db - สร้าง Prisma Client ซึ่งเป็นไลบรารีที่ใช้ในการโต้ตอบกับฐานข้อมูล
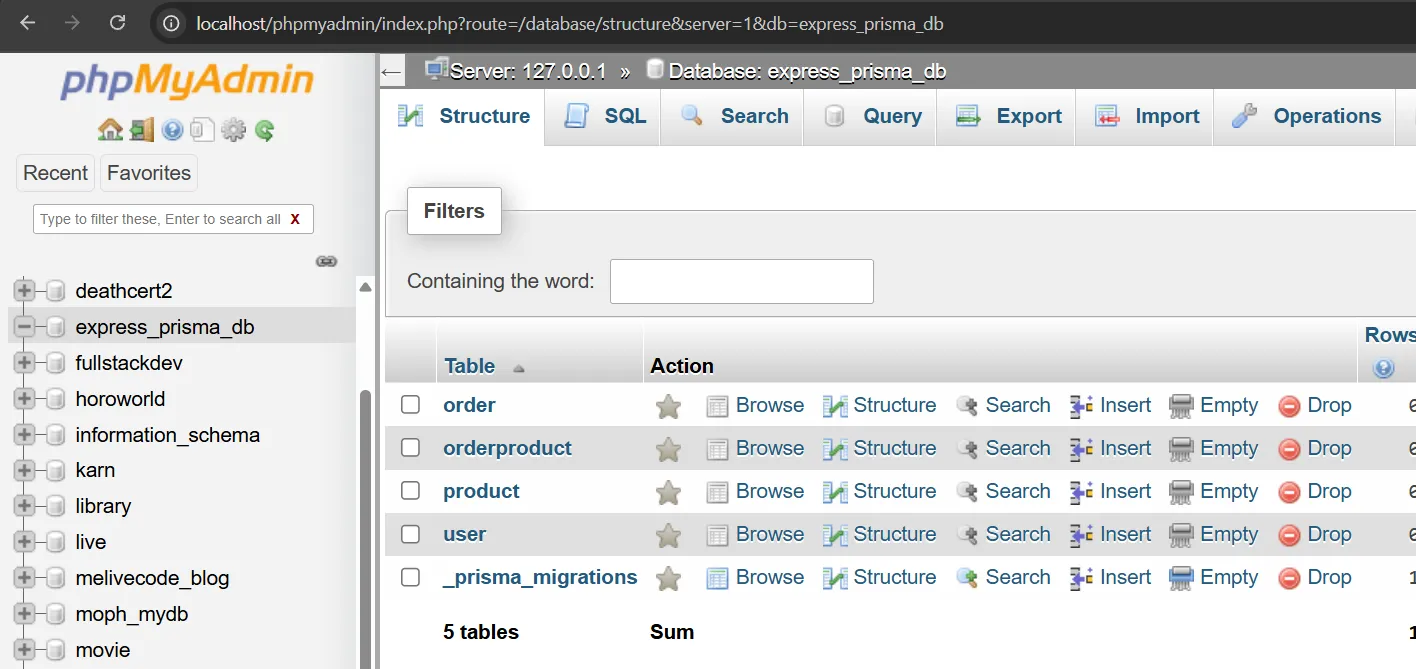
ดูผลลัพธ์ได้ที่ฐานข้อมูล express_prisma_db ที่ http://localhost/phpmyadmin ↗
7. สร้างไฟล์ Prisma Client#
สร้างไฟล์ src/prisma.js (หรือ src/prisma.ts ถ้าใช้ TypeScript) เพื่อ export instance ของ Prisma Client ที่เราจะนำไปใช้ใน Express application:
// src/prisma.js
const { PrismaClient } = require('@prisma/client');
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
module.exports = prisma;8. สร้าง index.js พร้อม Express + Prisma Endpoints#
สร้างไฟล์ index.js ใน root project และเพิ่มโค้ดพื้นฐานของ Express server พร้อมกับ Prisma client ที่เราสร้างไว้:
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const cors = require('cors');
const prisma = require('./src/prisma'); // Import Prisma Client
const app = express();
const port = 5000; // Define port
// Middleware
app.use(cors());
app.use(bodyParser.json());
// Test route
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello! RESTful API is ready to use with Prisma');
});
// Add API endpoints below this line
// Start server
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://localhost:${port}`);
});เริ่มต้นและทดสอบ API Server:
node index.jsเปิดเว็บเบราว์เซอร์ไปที่ http://localhost:5000 ↗ จะเห็นข้อความ “Hello! RESTful API is ready to use with Prisma” ดังรูป
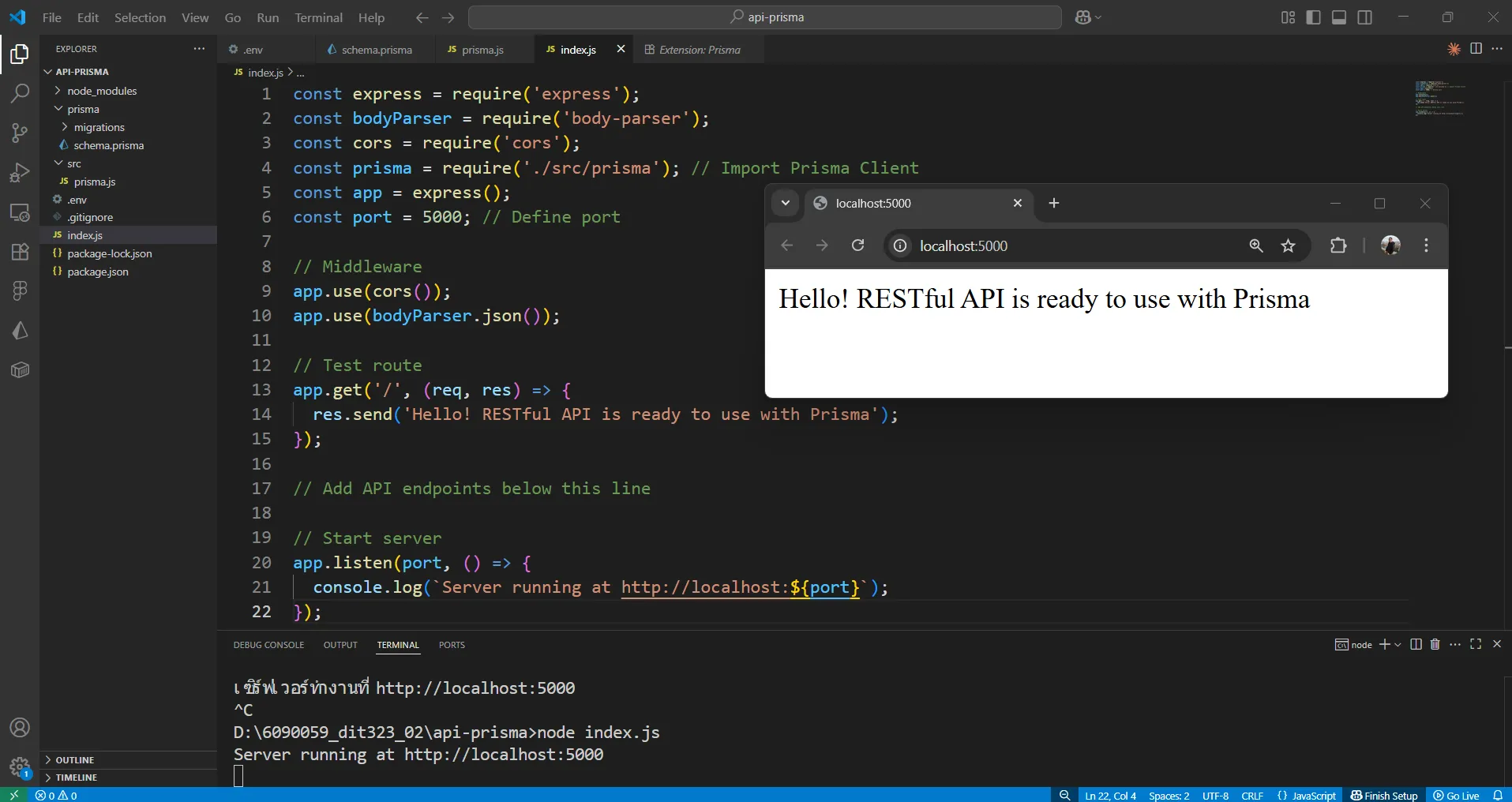
ต่อไปจะเป็นการเพิ่ม endpoints สำหรับ User, Product และ Order โดยใช้ Prisma ในการจัดการข้อมูล
8.1. User Endpoints#
เพิ่มโค้ดต่อไปนี้ในไฟล์ index.js ใต้ app.get('/')
// User Endpoints
// Read All Users
app.get('/users', async (req, res) => {
const users = await prisma.user.findMany();
res.json(users);
});
// Read One User
app.get('/users/:id', async (req, res) => {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
const user = await prisma.user.findUnique({ where: { id } });
if (!user) return res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' });
res.json(user);
});
// Create User
app.post('/users', async (req, res) => {
try {
const newUser = await prisma.user.create({ data: req.body });
res.status(201).json(newUser);
} catch (error) {
// Case where username or email is duplicated
if (error.code === 'P2002') {
return res.status(409).json({ message: 'Username or email already exists' });
}
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error creating user', error: error.message });
}
});
// Update User
app.put('/users/:id', async (req, res) => {
try {
const updated = await prisma.user.update({
where: { id: parseInt(req.params.id) },
data: req.body
});
res.status(200).json(updated);
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'P2025') { // Record not found
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' });
}
if (error.code === 'P2002') { // Unique constraint violation
return res.status(409).json({ message: 'Username or email already exists' });
}
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error updating user', error: error.message });
}
});
// Delete User
app.delete('/users/:id', async (req, res) => {
try {
const deleted = await prisma.user.delete({
where: { id: parseInt(req.params.id) }
});
res.status(200).json({ message: `User with ID ${deleted.id} deleted successfully` });
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'P2025') { // Record not found
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' });
}
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error deleting user', error: error.message });
}
});| HTTP Method | URI | วัตถุประสงค์ | Logic | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GET | /users | ดึงข้อมูลผู้ใช้ทั้งหมด | ใช้ prisma.user.findMany() เพื่อดึงข้อมูลทั้งหมด | รายการของ Object ผู้ใช้ทั้งหมด |
GET | /users/:id | ดึงข้อมูลผู้ใช้ตาม ID | ใช้ findUnique() จาก URL parameter id หากไม่พบจะคืนค่า 404 | Object ผู้ใช้ หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) |
POST | /users | สร้างผู้ใช้ใหม่ | req.body ควรมี fname, lname, username, email, avatar ใช้ prisma.user.create() | Object ผู้ใช้ที่สร้างใหม่ หรือ 409 (ซ้ำ) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
PUT | /users/:id | อัปเดตผู้ใช้ตาม ID | อัปเดตข้อมูลผู้ใช้โดยใช้ ID จาก URL และข้อมูลจาก Body จัดการข้อผิดพลาด (เช่น ไม่พบผู้ใช้ หรือข้อมูลซ้ำ) | Object ผู้ใช้ที่อัปเดต หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) หรือ 409 (ซ้ำ) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
DELETE | /users/:id | ลบผู้ใช้ตาม ID | ใช้ prisma.user.delete() ด้วย ID ที่กำหนด | Object ผู้ใช้ที่ถูกลบ หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API POST /users
วัตถุประสงค์ สร้างผู้ใช้ใหม่
Logic
req.bodyต้องประกอบด้วยข้อมูลต่อไปนี้:fname(ชื่อจริง),lname(นามสกุล),username(ชื่อผู้ใช้),email(อีเมล), และavatar(รูปโปรไฟล์)- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.user.create({ data: req.body })เพื่อบันทึกข้อมูลผู้ใช้ลงในฐานข้อมูล
Response
อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลผู้ใช้ที่ถูกสร้างขึ้นมาใหม่
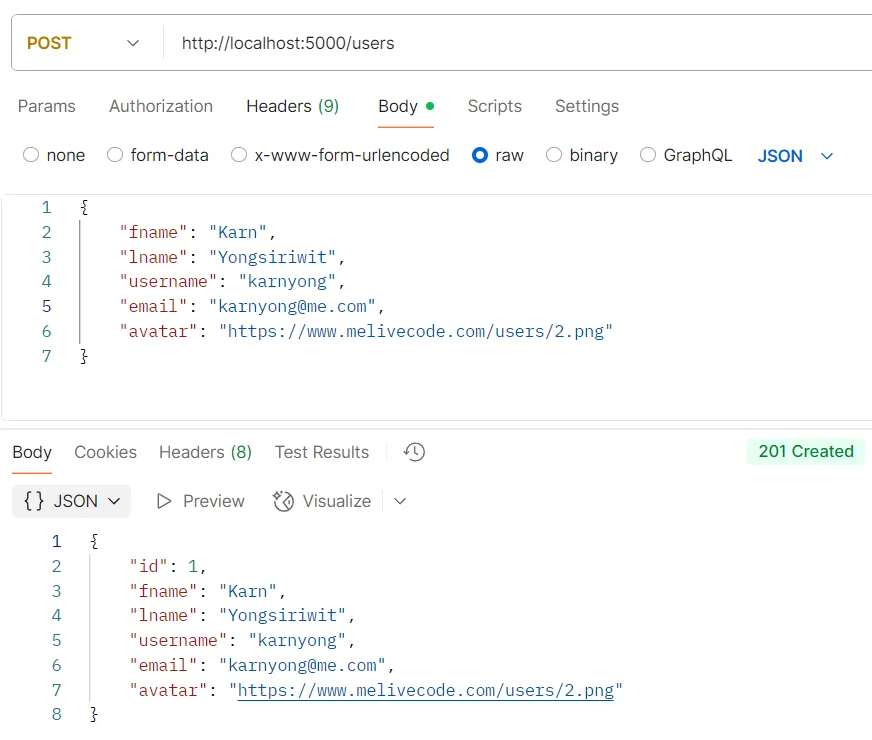
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /users
วัตถุประสงค์ ดึงข้อมูลผู้ใช้ทั้งหมด
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.user.findMany()เพื่อเรียกดูข้อมูลผู้ใช้ทั้งหมดจากฐานข้อมูล
Response
รายการอ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลผู้ใช้ทั้งหมด
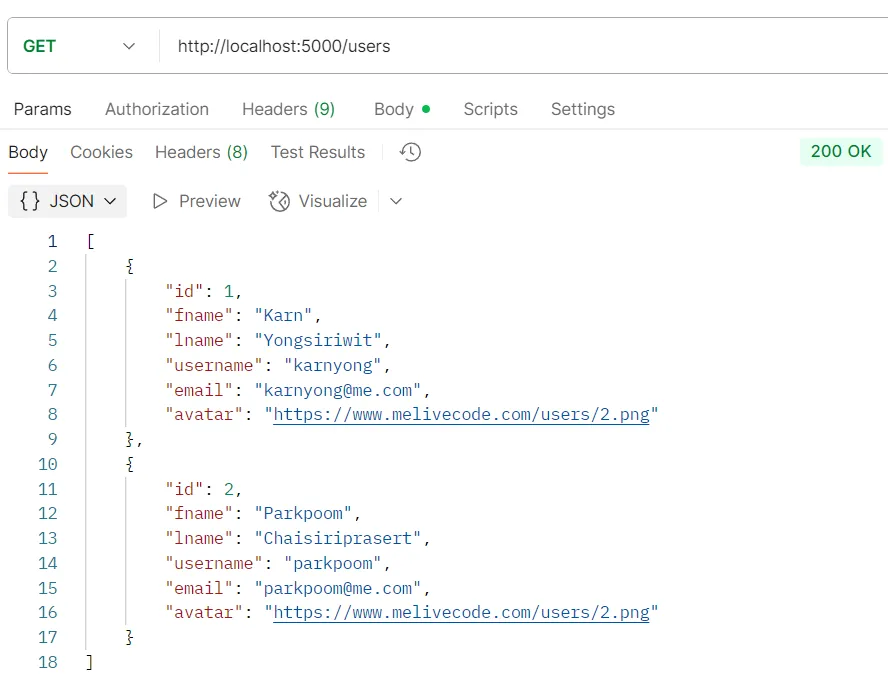
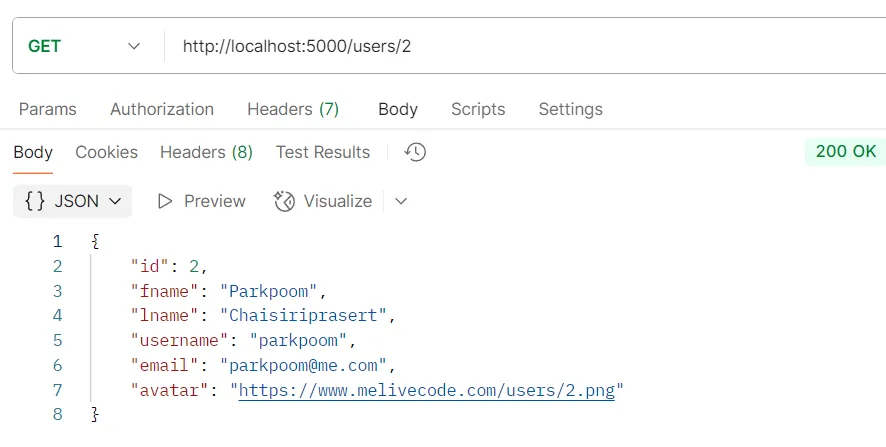
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /users/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ ดึงข้อมูลผู้ใช้รายเดียวด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
findUnique()โดยใช้ค่าidที่ได้จากพารามิเตอร์ใน URL - หากไม่พบผู้ใช้ ระบบจะส่งคืนสถานะ
404(Not Found)
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลผู้ใช้เพียงรายเดียว
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /users/:id
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /users/:id แบบไม่พบ user
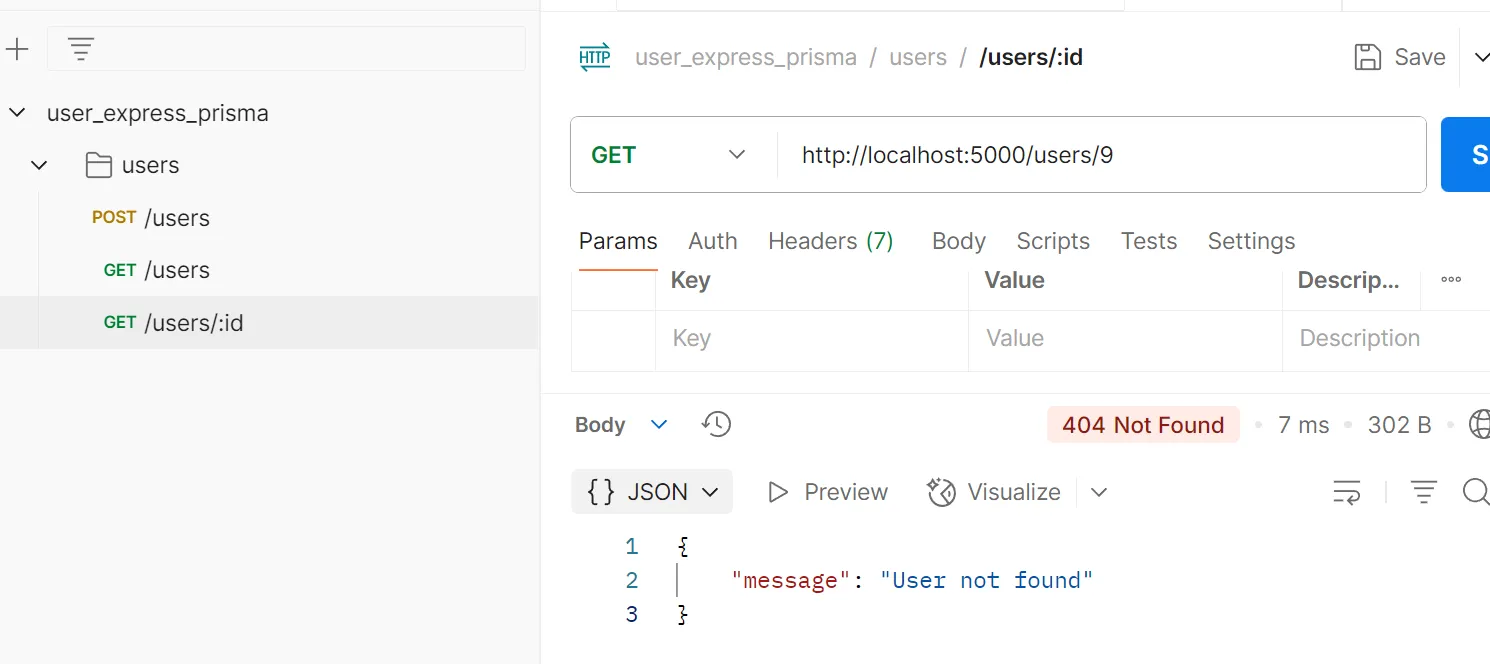
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API PUT /users/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ อัปเดตข้อมูลผู้ใช้ด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะแยกวิเคราะห์ (parse) ค่า
idจาก URL - ใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.user.update()พร้อมข้อมูลใหม่ที่ต้องการอัปเดต - มีการดักจับข้อผิดพลาด (error handling) เช่น กรณีที่ไม่พบผู้ใช้
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลผู้ใช้ที่ได้รับการอัปเดตแล้ว
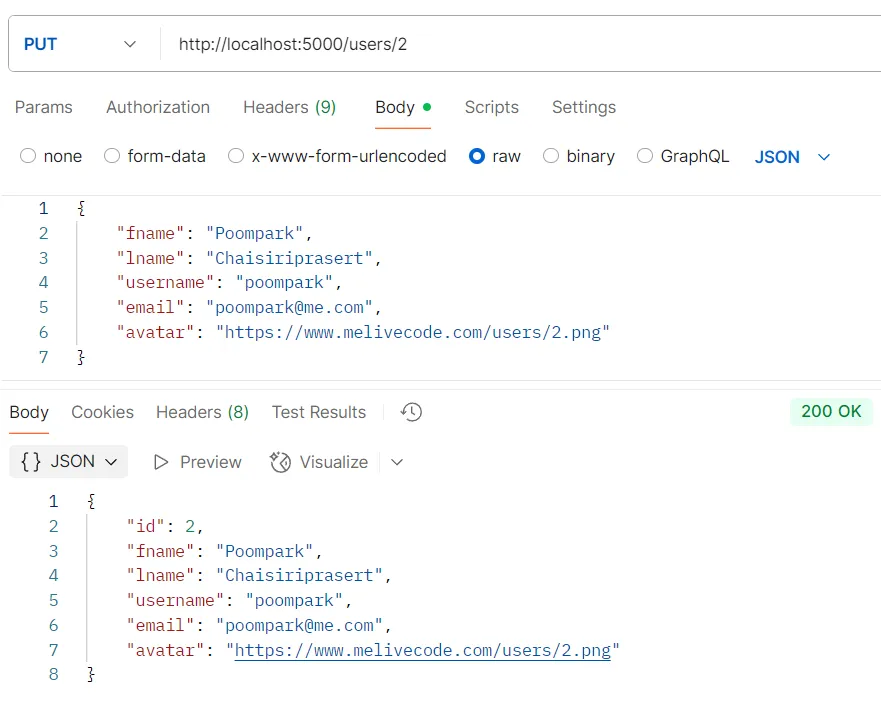
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API DELETE /users/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ ลบผู้ใช้ด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.user.delete()โดยใช้ค่า ID ที่ระบุ
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลผู้ใช้ที่ถูกลบไปแล้ว
8.2. Product Endpoints#
เพิ่มโค้ดต่อไปนี้ในไฟล์ index.js
// Product Endpoints
// Read All Products
app.get('/products', async (req, res) => {
const products = await prisma.product.findMany();
res.json(products);
});
// Read One Product
app.get('/products/:id', async (req, res) => {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
const product = await prisma.product.findUnique({ where: { id } });
if (!product) return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Product not found' });
res.json(product);
});
// Create Product
app.post('/products', async (req, res) => {
try {
const newProduct = await prisma.product.create({ data: req.body });
res.status(201).json(newProduct);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error creating product', error: error.message });
}
});
// Update Product
app.put('/products/:id', async (req, res) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
const updated = await prisma.product.update({
where: { id },
data: req.body
});
res.status(200).json(updated);
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'P2025') { // Record not found
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Product not found' });
}
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error updating product', error: error.message });
}
});
// Delete Product
app.delete('/products/:id', async (req, res) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
const deleted = await prisma.product.delete({ where: { id } });
res.status(200).json({ message: `Product with ID ${deleted.id} deleted successfully` });
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'P2025') { // Record not found
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Product not found' });
}
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error deleting product', error: error.message });
}
});| HTTP Method | URI | วัตถุประสงค์ | Logic | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GET | /products | ดึงข้อมูลสินค้าทั้งหมด | ใช้ prisma.product.findMany() เพื่อดึงข้อมูลทั้งหมด | รายการของ Object สินค้าทั้งหมด |
GET | /products/:id | ดึงข้อมูลสินค้าตาม ID | ใช้ findUnique() จาก URL parameter id หากไม่พบจะคืนค่า 404 | Object สินค้า หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) |
POST | /products | สร้างสินค้าใหม่ | req.body ควรมีข้อมูลสินค้า ใช้ prisma.product.create() | Object สินค้าที่สร้างใหม่ หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
PUT | /products/:id | อัปเดตสินค้าตาม ID | อัปเดตข้อมูลสินค้าโดยใช้ ID จาก URL และข้อมูลจาก Body จัดการข้อผิดพลาด (เช่น ไม่พบสินค้า) | Object สินค้าที่อัปเดต หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
DELETE | /products/:id | ลบสินค้าตาม ID | ใช้ prisma.product.delete() ด้วย ID ที่กำหนด | Object สินค้าที่ถูกลบ หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
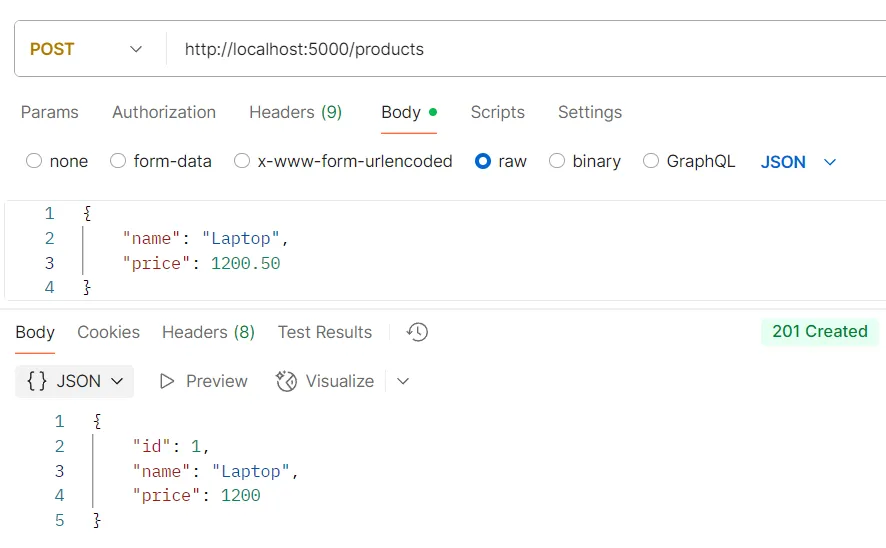
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API POST /products
วัตถุประสงค์ สร้างสินค้าใหม่
Logic
req.bodyต้องประกอบด้วยข้อมูลสินค้า- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.product.create({ data: req.body })เพื่อบันทึกข้อมูลสินค้าลงในฐานข้อมูล
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลสินค้าที่ถูกสร้างขึ้นมาใหม่
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /products
วัตถุประสงค์ ดึงข้อมูลสินค้าทั้งหมด
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.product.findMany()เพื่อเรียกดูข้อมูลสินค้าทั้งหมดจากฐานข้อมูล
Response รายการอ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลสินค้าทั้งหมด
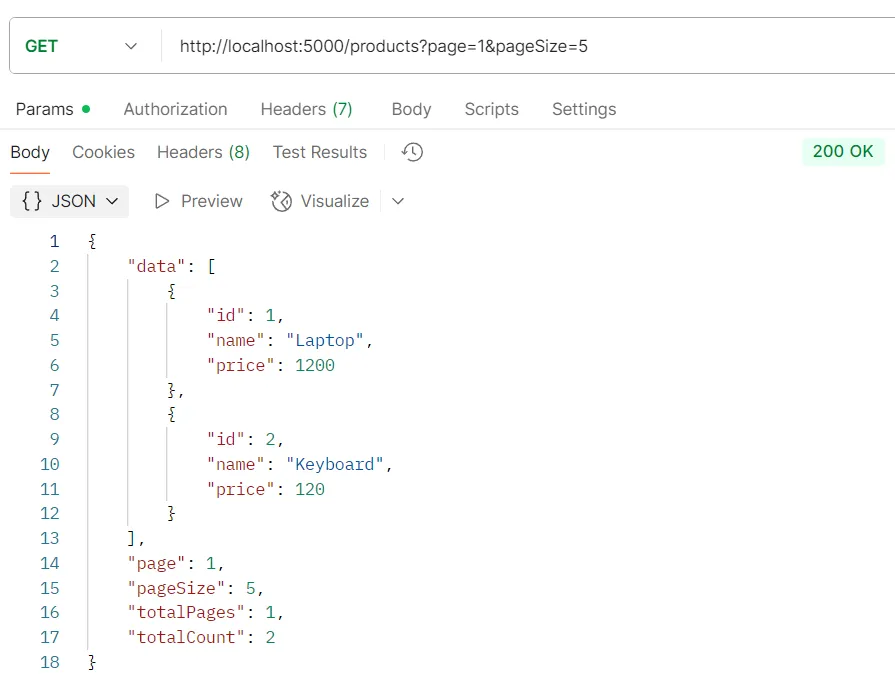
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /products/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ ดึงข้อมูลสินค้ารายเดียวด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
findUnique()โดยใช้ค่าidที่ได้จากพารามิเตอร์ใน URL - หากไม่พบสินค้า ระบบจะส่งคืนสถานะ
404(Not Found)
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลสินค้าเพียงรายเดียว
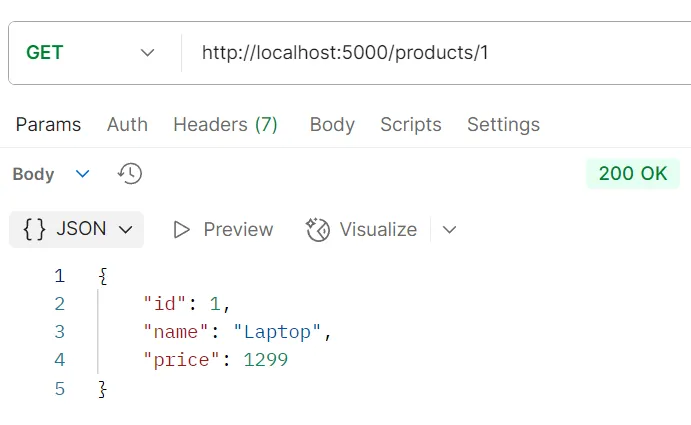
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API PUT /products/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ อัปเดตข้อมูลสินค้าด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะแยกวิเคราะห์ (parse) ค่า
idจาก URL - ใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.product.update()พร้อมข้อมูลใหม่ที่ต้องการอัปเดต - มีการดักจับข้อผิดพลาด (error handling) เช่น กรณีที่ไม่พบสินค้า
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลสินค้าที่ได้รับการอัปเดตแล้ว
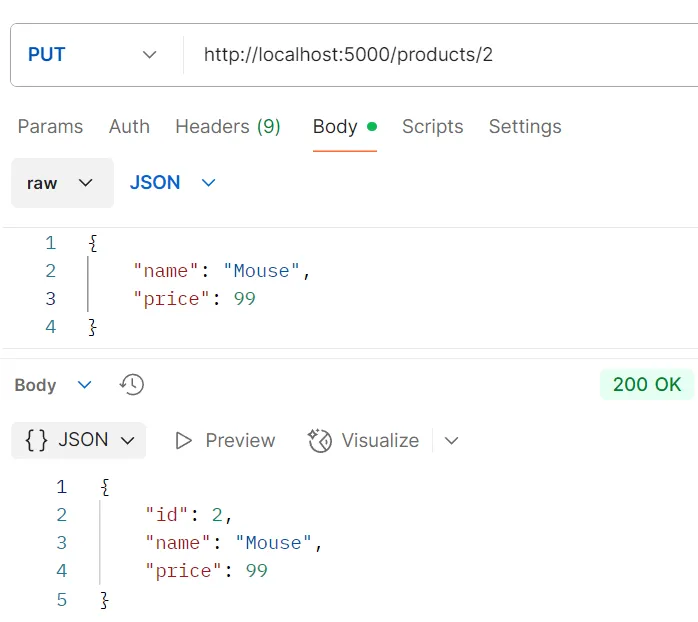
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API DELETE /products/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ ลบสินค้าด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.product.delete()โดยใช้ค่า ID ที่ระบุ
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลสินค้าที่ถูกลบไปแล้ว
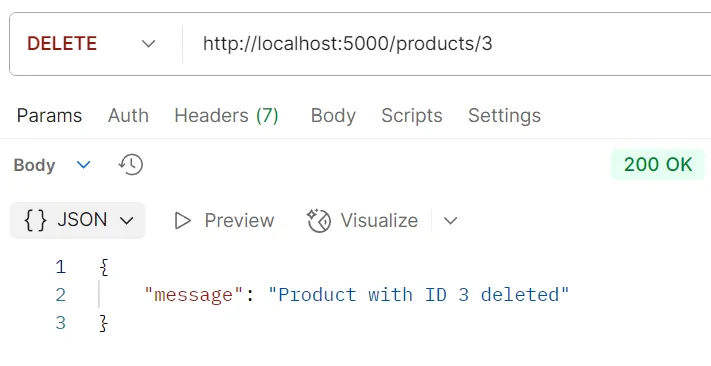
8.3. Order Endpoints#
เพิ่มโค้ดต่อไปนี้ในไฟล์ index.js
// Order Endpoints
// Read All Orders
app.get('/orders', async (req, res) => {
const orders = await prisma.order.findMany({
include: {
user: true,
products: { include: { product: true } }
}
});
res.json(orders);
});
// Read One Order
app.get('/orders/:id', async (req, res) => {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
const order = await prisma.order.findUnique({
where: { id },
include: {
user: true,
products: { include: { product: true } }
}
});
if (!order) return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Order not found' });
res.json(order);
});
// Create Order
app.post('/orders', async (req, res) => {
const { userId, productIds } = req.body;
try {
const newOrder = await prisma.order.create({
data: {
userId,
products: {
create: productIds.map(pid => ({ productId: pid }))
}
},
include: {
products: { include: { product: true } },
user: true
}
});
res.status(201).json(newOrder);
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'P2003') { // Foreign key constraint failed
return res.status(400).json({ message: 'Invalid user ID or product ID' });
}
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error creating order', error: error.message });
}
});
// Update Order
app.put('/orders/:id', async (req, res) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
const { userId, productIds } = req.body;
const updated = await prisma.order.update({
where: { id },
data: {
userId,
products: {
deleteMany: {},
create: productIds.map((productId) => ({
product: { connect: { id: productId } }
}))
}
},
include: {
products: { include: { product: true } },
user: true
}
});
res.status(200).json(updated);
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'P2025') { // Record not found
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Order not found' });
}
if (error.code === 'P2003') { // Foreign key constraint failed
return res.status(400).json({ message: 'Invalid user ID or product ID' });
}
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error updating order', error: error.message });
}
});
// Delete Order
app.delete('/orders/:id', async (req, res) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
// Delete related OrderProduct records first
await prisma.orderProduct.deleteMany({
where: { orderId: id }
});
// Then delete the order
const deleted = await prisma.order.delete({ where: { id } });
res.status(200).json({ message: `Order with ID ${deleted.id} deleted successfully` });
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'P2025') { // Record not found
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Order not found' });
}
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error deleting order', error: error.message });
}
});| HTTP Method | URI | วัตถุประสงค์ | Logic | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GET | /orders | ดึงข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมด | ใช้ prisma.order.findMany() พร้อม include ข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า | รายการของ Object คำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมดพร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า |
GET | /orders/:id | ดึงข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อตาม ID | ใช้ findUnique() จาก URL parameter id พร้อม include หากไม่พบจะคืนค่า 404 | Object คำสั่งซื้อพร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) |
POST | /orders | สร้างคำสั่งซื้อใหม่ | req.body ต้องมี userId และ productIds ใช้ prisma.order.create() พร้อมสร้างความสัมพันธ์กับสินค้า | Object คำสั่งซื้อที่สร้างใหม่พร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า หรือ 400 (ข้อมูลไม่ถูกต้อง) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
PUT | /orders/:id | อัปเดตคำสั่งซื้อตาม ID | อัปเดตข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อ ลบสินค้าเก่าและเพิ่มสินค้าใหม่ จัดการข้อผิดพลาด | Object คำสั่งซื้อที่อัปเดตพร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) หรือ 400 (ข้อมูลไม่ถูกต้อง) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
DELETE | /orders/:id | ลบคำสั่งซื้อตาม ID | ลบข้อมูลความสัมพันธ์ OrderProduct ก่อน จากนั้นลบคำสั่งซื้อ | ข้อความยืนยันการลบ หรือ 404 (ไม่พบ) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
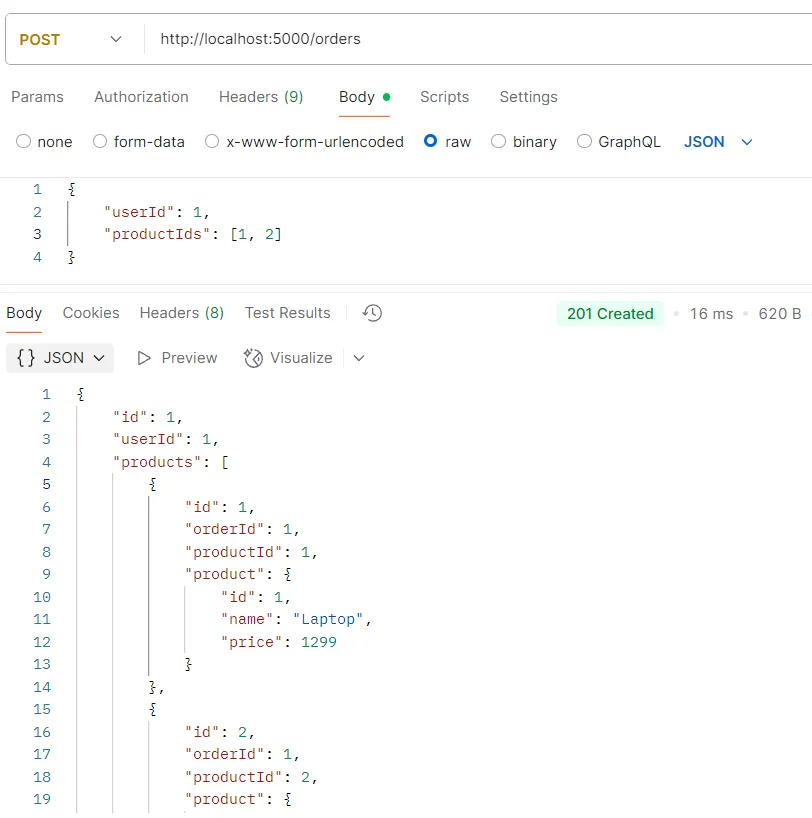
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API POST /orders
วัตถุประสงค์ สร้างคำสั่งซื้อใหม่
Logic
req.bodyต้องประกอบด้วยข้อมูลต่อไปนี้:userId(รหัสผู้ใช้) และproductIds(รายการรหัสสินค้า)- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.order.create()เพื่อสร้างคำสั่งซื้อพร้อมเชื่อมโยงกับสินค้าที่เลือก - ข้อมูลจะถูกส่งกลับพร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และรายละเอียดสินค้า
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อที่ถูกสร้างขึ้นมาใหม่พร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า
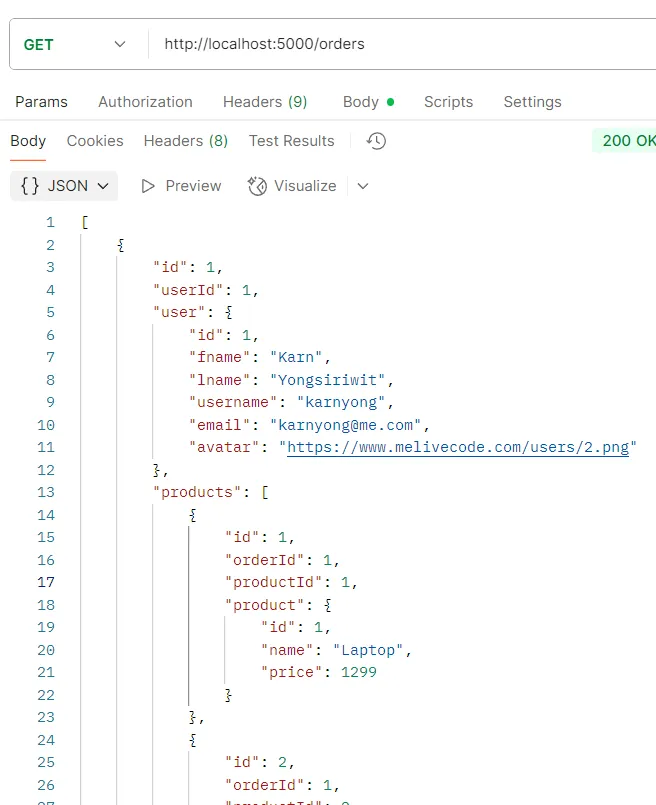
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /orders
วัตถุประสงค์ ดึงข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมด
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.order.findMany()พร้อมincludeเพื่อดึงข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมดพร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า
Response รายการอ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมดพร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า
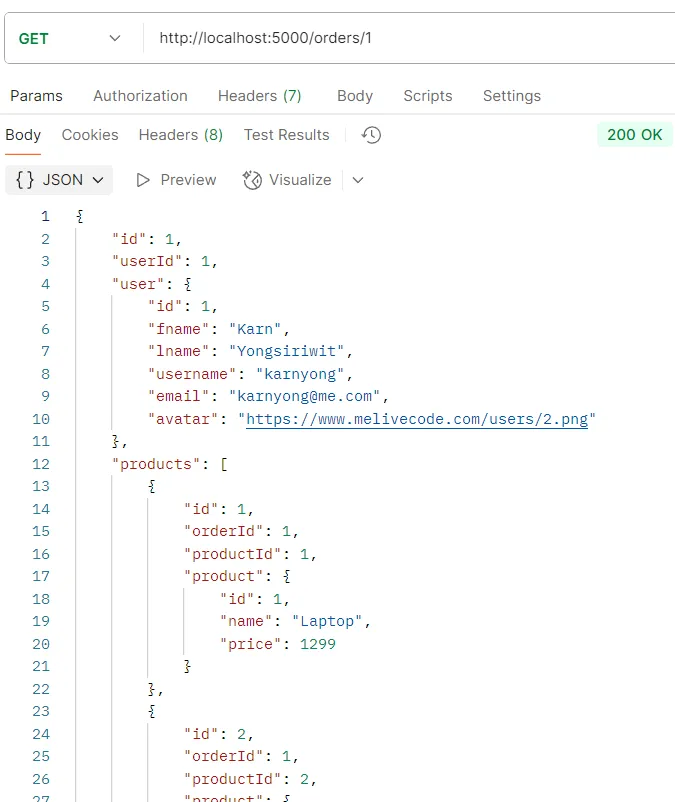
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /orders/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ ดึงข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อรายเดียวด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
findUnique()โดยใช้ค่าidที่ได้จากพารามิเตอร์ใน URL - ใช้
includeเพื่อดึงข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้าที่เกี่ยวข้อง - หากไม่พบคำสั่งซื้อ ระบบจะส่งคืนสถานะ
404(Not Found)
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อเพียงรายเดียวพร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า
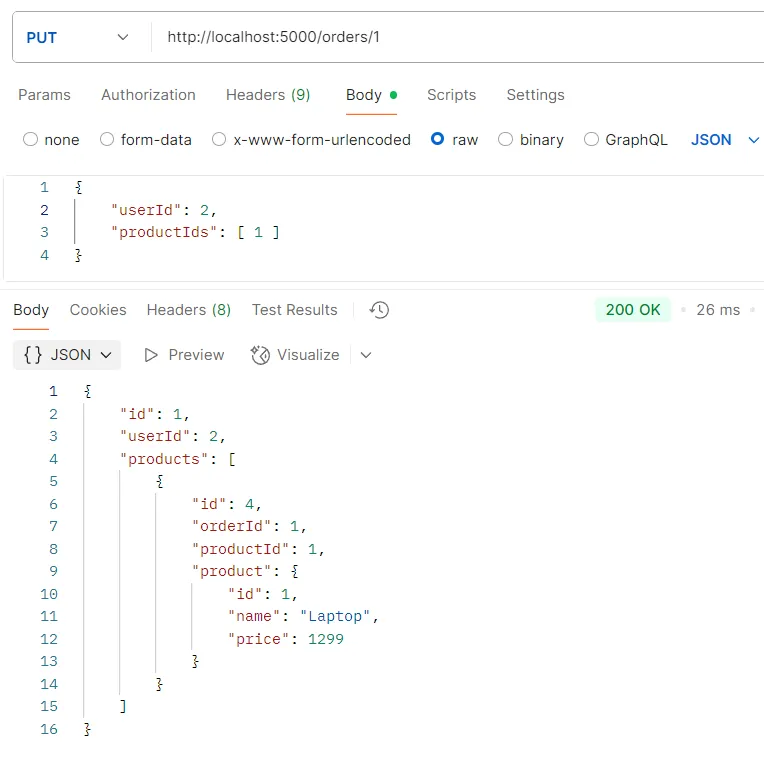
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API PUT /orders/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ อัปเดตข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะแยกวิเคราะห์ (parse) ค่า
idจาก URL - ใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.order.update()พร้อมข้อมูลใหม่ - ลบความสัมพันธ์กับสินค้าเก่าทั้งหมด (
deleteMany: {}) และสร้างความสัมพันธ์ใหม่กับสินค้าที่เลือก - มีการดักจับข้อผิดพลาด (error handling) เช่น กรณีที่ไม่พบคำสั่งซื้อ
Response อ็อบเจกต์ของข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อที่ได้รับการอัปเดตแล้วพร้อมข้อมูลผู้ใช้และสินค้า
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API DELETE /orders/:id
วัตถุประสงค์ ลบคำสั่งซื้อด้วย ID
Logic
- ระบบจะลบข้อมูลในตาราง
orderProductที่เกี่ยวข้องกับคำสั่งซื้อนี้ก่อน - จากนั้นใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.order.delete()เพื่อลบคำสั่งซื้อ
Response ข้อความยืนยันการลบคำสั่งซื้อ
 |
|
8.4. Nested Endpoints#
เพิ่มโค้ดต่อไปนี้ในไฟล์ index.js เพื่อสร้าง endpoints สำหรับทรัพยากรแบบซ้อน
// Relationship Endpoints
// Get Orders by User ID
app.get('/users/:id/orders', async (req, res) => {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
try {
const user = await prisma.user.findUnique({ where: { id } });
if (!user) return res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' });
const orders = await prisma.order.findMany({
where: { userId: id },
include: {
products: { include: { product: true } },
user: true
}
});
res.json(orders);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error fetching user orders', error: error.message });
}
});
// Get Products by Order ID
app.get('/orders/:id/products', async (req, res) => {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
try {
const order = await prisma.order.findUnique({
where: { id },
include: { products: { include: { product: true } } }
});
if (!order) return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Order not found' });
const products = order.products.map(p => p.product);
res.json(products);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Error fetching order products', error: error.message });
}
});| HTTP Method | URI | วัตถุประสงค์ | Logic | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GET | /users/:id/orders | ดึงคำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมดของผู้ใช้ | ตรวจสอบว่าผู้ใช้มีอยู่จริง จากนั้นใช้ prisma.order.findMany() กรองด้วย userId | รายการ Object คำสั่งซื้อของผู้ใช้นั้นๆ พร้อมข้อมูลสินค้า หรือ 404 (ไม่พบผู้ใช้) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
GET | /orders/:id/products | ดึงสินค้าทั้งหมดในคำสั่งซื้อ | ใช้ findUnique() เพื่อหาคำสั่งซื้อพร้อมสินค้า จากนั้น map เอาเฉพาะข้อมูลสินค้า | รายการ Object สินค้าในคำสั่งซื้อนั้นๆ หรือ 404 (ไม่พบคำสั่งซื้อ) หรือ 500 (ข้อผิดพลาด) |
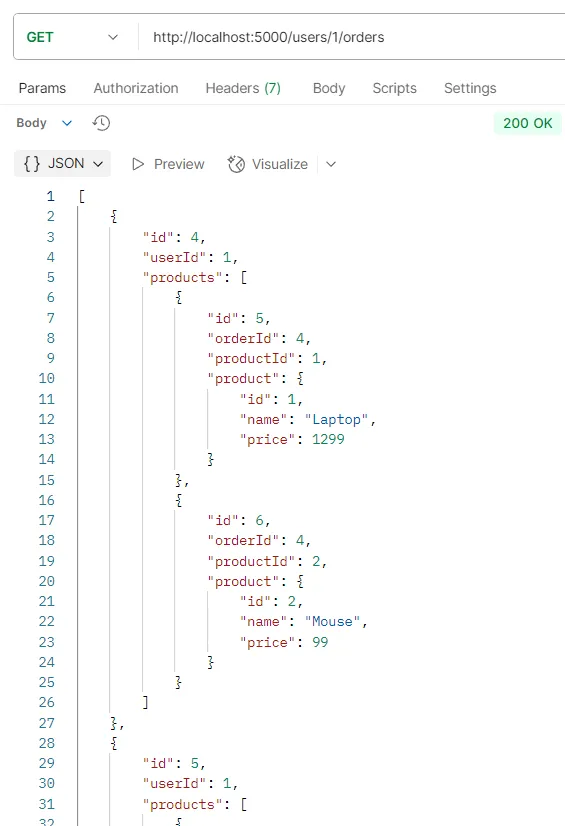
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /users/:id/orders
วัตถุประสงค์ ดึงข้อมูลคำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมดของผู้ใช้คนหนึ่ง
Logic
- ระบบจะตรวจสอบว่าผู้ใช้ที่มี
idตามที่ระบุมีอยู่ในฐานข้อมูลหรือไม่ - หากพบผู้ใช้ ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
prisma.order.findMany()โดยกรองด้วยuserId - ใช้
includeเพื่อดึงข้อมูลสินค้าและผู้ใช้ที่เกี่ยวข้อง - หากไม่พบผู้ใช้ ระบบจะส่งคืนสถานะ
404(User not found)
Response รายการอ็อบเจกต์ของคำสั่งซื้อทั้งหมดของผู้ใช้นั้นๆ พร้อมข้อมูลสินค้า
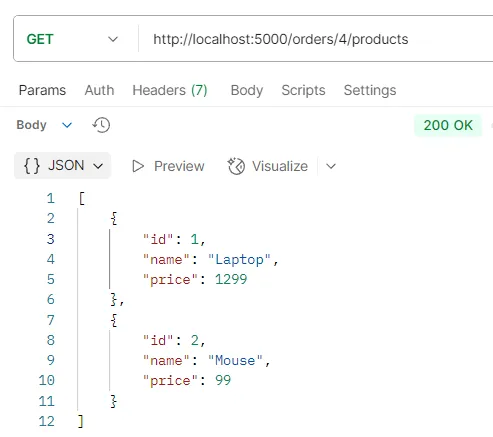
ตัวอย่างการทดสอบ API GET /orders/:id/products
วัตถุประสงค์ ดึงข้อมูลสินค้าทั้งหมดในคำสั่งซื้อหนึ่งๆ
Logic
- ระบบจะใช้คำสั่ง
findUnique()โดยใช้ค่าidของคำสั่งซื้อที่ได้จากพารามิเตอร์ใน URL - ใช้
includeเพื่อดึงข้อมูลสินค้าที่เกี่ยวข้องกับคำสั่งซื้อ - ใช้
map()เพื่อแปลงข้อมูลให้ได้เฉพาะรายละเอียดสินค้า (p.product) - หากไม่พบคำสั่งซื้อ ระบบจะส่งคืนสถานะ
404(Order not found)
Response รายการอ็อบเจกต์ของสินค้าทั้งหมดที่อยู่ในคำสั่งซื้อนั้นๆ
หมายเหตุเพิ่มเติม
Relationship Endpoints เหล่านี้ช่วยให้การเข้าถึงข้อมูลที่เกี่ยวข้องกันมีความสะดวกมากขึ้น:
/users/:id/orders- เหมาะสำหรับการแสดงประวัติการสั่งซื้อของลูกค้าแต่ละคน/orders/:id/products- เหมาะสำหรับการแสดงรายการสินค้าในใบสั่งซื้อเฉพาะ
ทั้งสอง endpoints นี้ช่วยลดความซับซ้อนในการเรียกใช้ข้อมูลจากฝั่ง frontend และทำให้ API มีความยืดหยุ่นในการใช้งานมากขึ้น
การทำความเข้าใจโครงสร้าง API และการทำงานของ Prisma จะช่วยให้เข้าใจหลักการพัฒนา Web Application ได้ดีมากขึ้นครับ
